When doing quantitative analysis from non-volumetric dried blood spots, a few additional parameters should be considered. Especially hematocrit (percentage of red blood cells in the blood) effects should be addressed, which could lead to a volume-area bias or a hematocrit dependent extraction recovery.
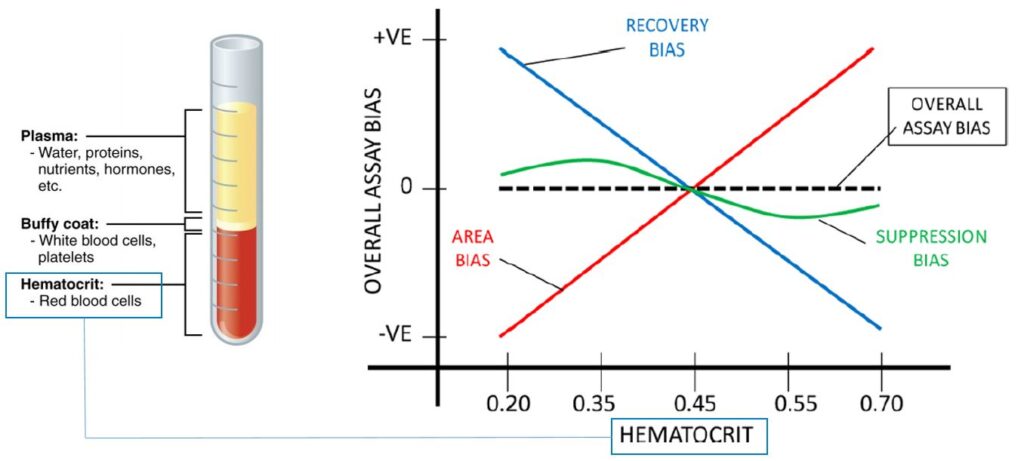
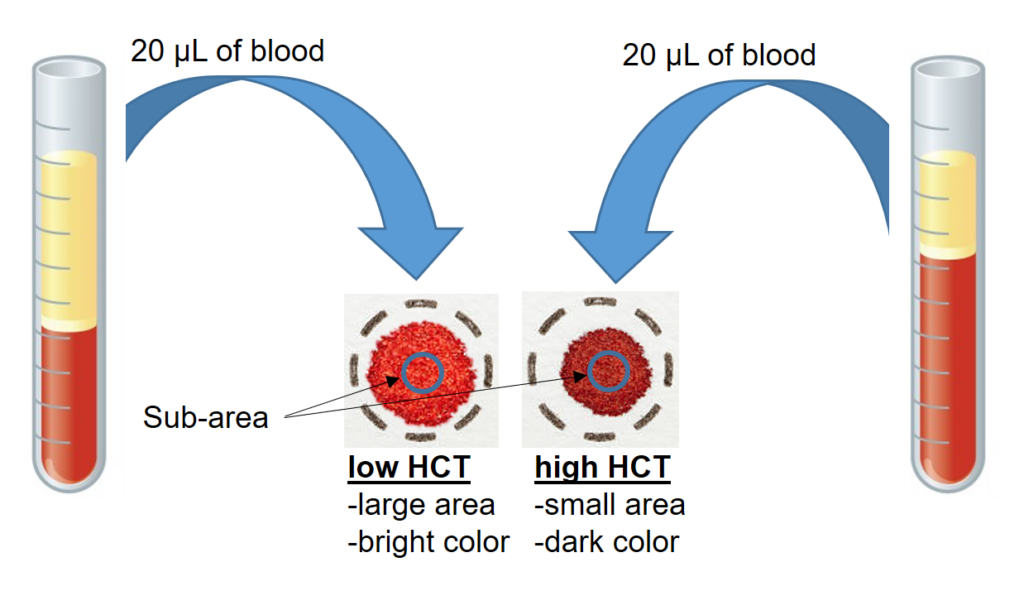
The volume-area bias describes the different extraction volume of blood in sub-areas from DBS with the same volume but different hematocrit (figure above). The recovery bias describes the effect of different extraction recovery of two DBS with different hematocrit.
To address the hematocrit (HCT) related volume-area bias, CAMAG developed a fully automated HCT detection module that allows rapid and simple DBS HCT assessment and normalization. The working principle is based on non-destructive, reflectance spectroscopy and has been fully validated. Being embedded within the automated CAMAG DBS-MS 500 HCT, the setup permits the high-throughput analysis of the DBS’ reflectance at a specific wavelength, which correlates with the HCT of the DBS. The novel workflow makes the necessity of volumetric sampling for quantitative DBS analysis obsolete: By using a fixed extraction area that is completely saturated with blood, eluting from the center of each DBS, and correcting for the HCT of the target analyte. The HCT correction compensates for the blood volume within the fixed sampling area, as the spreading area of blood on the filter paper is HCT dependent.
The HCT related recovery bias is addressed by spraying the internal standard directly onto the DBS prior extraction. This has been described as the gold standard in literature and adds the internal standard at the earliest time point of the workflow.
A third effect is the coffee stain effect that describes a faster drying at the border zones of the DBS. As the DBS-MS 500 HCT always detects the DBS center and extracts directly from the center, this effect is nullified by using the automation as well.
To summarize, all HCT related effects are nullified by using the DBS-MS 500 HCT automation, the hematocrit detection module and the internal standard spraying unit. The target analytes can be quantified by using this information and according algorithms and knowledge of the exact sample volume is not necessary.
Luginbühl M, Fischer Y, Gaugler S. Fully Automated Optical Hematocrit Measurement from Dried Blood Spots, Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 2020. doi:10.1093/jat/bkaa189
Luginbühl M, Gaugler S. Dried blood spots for antidoping: Why just going volumetric may not be sufficient. Drug Testing and Analysis. 2021; 13: 69–73. doi:10.1002/dta.2977
Luginbühl M, Stöth F, Weinmann W, Gaugler S. Fully Automated Correction for the Hematocrit Bias of Non-Volumetric Dried Blood Spot Phosphatidylethanol Analysis. Alcohol. 2021
Capiau et al., Official International Association for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Clinical Toxicology Guideline: Development and Validation of Dried Blood Spot-Based Methods for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, Ther Drug Monit. 2019 Aug;41(4):409-430 doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000643